Here are examples of queries in Genomicus that illustrate key features of the
browser and highlight the benefits of examining comparative genomic
data in a broad phylogenetic perspective.
-
Fgf1a in the zebrafish genome on chromosome 14 —
PhyloView, rooted at the Euteleostomi ancestor
The red square node shows that a duplication of the ancestral Fgf1a
gene took place in the ancestral Clupeocephala genome. The zebrafish
paralog of Fgf1a is on chromosome 21 (Fgf1b), but the display shows
that all other fish also contain two copies, Fgf1a and Fgf1b. Most
strikingly, many gene that are neighbours of Fgf1a also have paralogs
in the neighborhood of its paralog Fgf1b, and this is true in all
sequenced fish genomes. One can therefore conclude (as in the Krox20
example in mouse, above) that this situation is reminiscent of a
large segmental duplication - or in this case - of the whole genome
duplication that took place in the ancestor of ray-finned fish (so-
called «3R» duplication). Interestingly, Fgf1 in tetrapodes is also
surrounded by many genes that are still in the vicinity of the
zebrafish Fgf1a and Fgf1b gene.
-
Phox2b
PhyloView, rooted at the Euteleostomi ancestor
One notices that this region is remarkably well conserved in the
descendents of the ancestral amniota, and that Phox2b is surrounded
by a high density of conserved non coding elements (CNEs) identified
between chicken and several mammals (red symbols in intergenic regions).
-
Unc-50 in C-elegans on chromosome III —
PhyloView, rooted at the Bilateria ancestor
This relatively simple situation shows that the Unc-50 gene (green)
possesses orthologs in most vertebrates and that a neighbouring gene
NP_499273.3 (blue) also has an ortholog in these same species, and
that both remains nearly adjacent in all these genomes, except in
fish. This is remarkable given the very large cumulated evolutionary
distance that separate the different extant genomes.
-
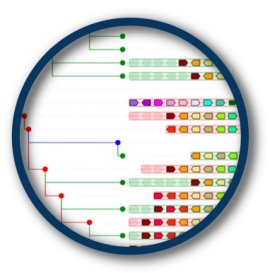
Krox20 (Egr2) in the mouse genome on chromosome 10 —
PhyloView
The expended red square nodes shows three successive duplications of the
ancestral Krox20 gene in the ancestral bony vertebrate (Euteleostomi)
genome. By following the branch leading to the most recent copy on
mouse chromosome 14 (gene Egr3), one immediately see that this locus
contains many other paralogs of genes that are neighbours of Krox20
(colored genes with white outlines). This strongly suggest that the
two regions on mouse chromosome 14 and 10 originate from a single
event that duplicated all the genes in the ancestral region. This
situation is a typical signature of the whole genome duplication(s)
that took place just before the bony vertebrate radiation (so-called
«2R» duplications).

 Contact us.
Contact us.