Here are examples of queries in Genomicus that illustrate key features of the
browser and highlight the benefits of examining comparative genomic
data in a broad phylogenetic perspective.
-
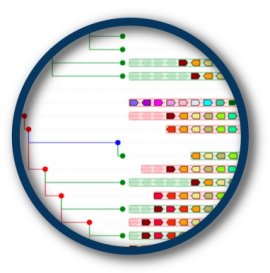
The BRADI2G34810 gene on Brachypodium chromosome 2 (PhyloView)
The BRADI2G34810 gene on Brachypodium chromosome 2 is in a region relatively well conserved with other monocots. A red node in Poacea indicates an ancestral duplication of this gene. The paralog of BRADI2G34810 (BRADI2G12420) is also on chromosome 2 but in a much more telomeric position, and many surrounding genes of BRADI2G34810 also possess paralogs in this telomeric locus, indicative of an "en-bloc" duplication of a chromosome segment. The ancestral duplication is confirmed by the fact that many other monocots (maize, sorghum, rice) possess the same "paralogon". Dicots possess an ortholog of the brachypodium BRADI2G34810 gene but as expected, in an orthologous chromosome segment showing a less well conserved synteny. However, a few genes orthologous to neighbours of BRADI2G34810 do remain in dicots, a testimony of the common origin of the region in monocots and dicots since the ancestral Magnoliophyta genome.
-
The BGIOSGA025228 gene on rice (indica) chromosome 7 (AlignView)
This example shows that the region of indica chromosome 7 is completely collinear with the orthologous region of japonica chromosome 7, except for a few (6) genes that are either deleted or not yet annotated in japonica. All the orthologs of the region shown from Oryza sativa indica are also located on a single chromosome in Brachypodium (chr 1), and mainly on chromosome 2 in Sorghum, although 3 genes are also on sorghum chromosome 1. In maize on the other hand, while the indica locus is mainly present in two copies on maize chromosomes 7 and 2, many orthologs are dispersed on multiple other chromosomes.



 Contact us.
Contact us.